
Inductive learning, also known as discovery learning, is a process where the learner discovers rules by observing examples. This is different from deductive learning, where students are given rules that they then need to apply.
Continue reading


Inductive learning, also known as discovery learning, is a process where the learner discovers rules by observing examples. This is different from deductive learning, where students are given rules that they then need to apply.
Continue reading

The word “syntax” describes the rules we use to put words together to make sentences. It shows the relationship between words and their meaning in sentences. Continue reading

Functional language is language that you need in different day-to-day situations. For example: greeting, introducing yourself, asking for or giving advice, explaining rules, apologising, or agreeing and disagreeing. Any one of these functions can have a number of different exponents, or fixed expressions. For example, giving advice we could say: Continue reading

Skills relate to different aspects of using language; such as listening, reading, writing or speaking. Skills are our ability to do these things. They are usually divided into two types: receptive and productive. Continue reading

Task-based language learning is an approach where the planning of learning materials and teaching sessions are based around doing a task. In education, a task refers to an activity where communication is necessary: for example; deciding something, solving a problem, designing or organising something, or Continue reading
Flash cards are not new to teaching and learning. Teachers have been using flash cards, or flashcards, or flip cards of one kind or another to teach vocabulary and other concepts for a very long time. Continue reading
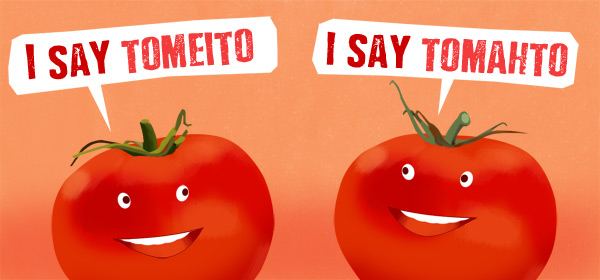
A person’s accent is the product of where they are from and, in some cases, their social and educational background. Continue reading

You’ve probably heard of the terms “flipped classroom” and “blended learning course” in the context of online learning, but what do they really mean? Are they the same? Are they different and, if so, how? Continue reading